Pushing the limits of conventional computing by putting processing power closer to the source, Edge Computing is transforming how several sectors handle and process data. As a matter of fact, it is revolutionizing industries by reducing latency and enhancing efficiency. It gives current information, which helps in the quick decision-making process and enhances the business operations. Furthermore, this technology is revolutionizing industries like healthcare, manufacturing, retail and autonomous vehicles. With more and more IoT devices being deployed, the demand for quicker and more dependable systems is on the rise. Edge computing offers a powerful solution to address these needs. By processing data locally, it lowers costs and boosts performance, making systems more efficient and dependable.
This blog will cover the Edge Computing Global Implications and also how it is influencing the direction of technology, from more effective supply chains to smarter cities.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a breakthrough IT architecture that allows faster and more effective operations by processing data closer to its source. Since, it disperses processing and storage to the network’s edge, such as user systems, edge servers, or IoT devices, as opposed to depending entirely on centralized data centers. Moreover, by processing data locally, this method guarantees real-time insights while minimizing latency and bandwidth use. It is especially useful for managing the massive data streams produced by IoT sensors and distant devices in difficult-to-reach places.
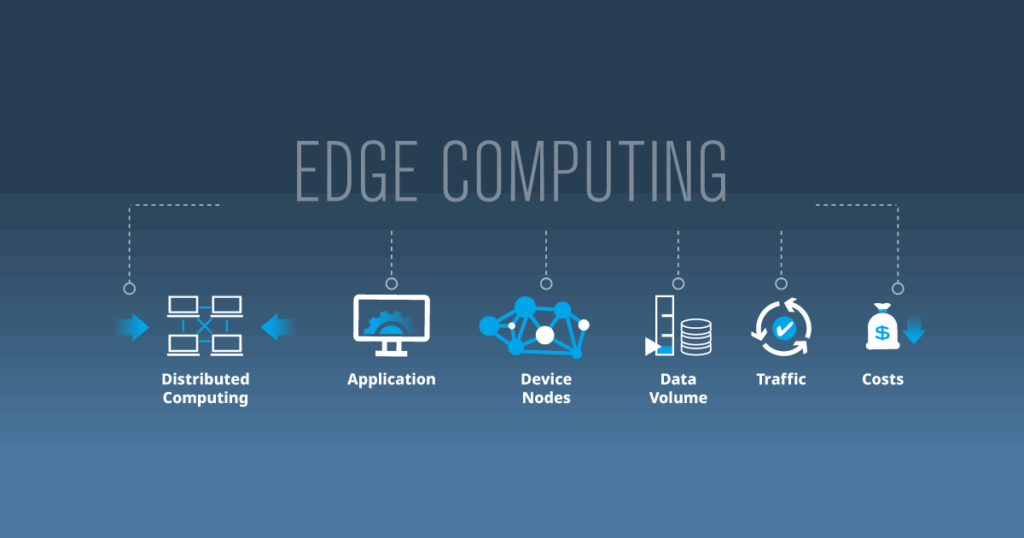
Edge computing is transforming how companies handle data by tackling issues like bandwidth constraints and network outages, producing actionable findings more quickly and consistently. Edge use cases continue to transform contemporary computing, from smart cities to retail.
How Does Edge Computing Work?
Edge computing splits computing capacity to process data closer to its source, lowering latency, increasing speed, and providing immediate insights. Edge computing allows distant devices to function as little data centers, processing data locally, in contrast to conventional models that depend on centralized data centers. This method guarantees smooth, real-time outcomes, facilitates operations in places with poor internet, and reduces dependency on cloud computing. Businesses may improve and speed up procedures by combining edge and cloud computing, which makes edge computing revolutionary for effectively managing enormous data volumes.
What are Global Implications of Edge Computing?
The future of technology is being transformed by edge computing in a number of innovative ways. Experts are already noticing it because it is expected to reach $317 billion in worldwide value by 2026. In sectors like healthcare and autonomous vehicles, where real-time processing and decision-making are important, it might be needed. Let’s explore some of the Global Implications of Edge Computing that is changing different industries and possible implications for the future in more detail.
1: Monitoring Patient Health with Real-Time Data Processing:
Edge computing is revolutionizing the healthcare sector by enabling real-time data processing from IoT devices such as smart medical instruments, glucose monitors, and wearable trackers. For instance, sensors can monitor blood pressure, pulse rate, or oxygen levels and alert medical personnel right away to any abnormalities. Other than that, it improves privacy and lessens dependency on external clouds by processing data locally. It also enables advanced analytics to identify problems, analyze results, and customize interventions effectively. Additionally, it also makes 360-degree patient dashboards and real-time warnings possible, which enhances patient care and visibility.
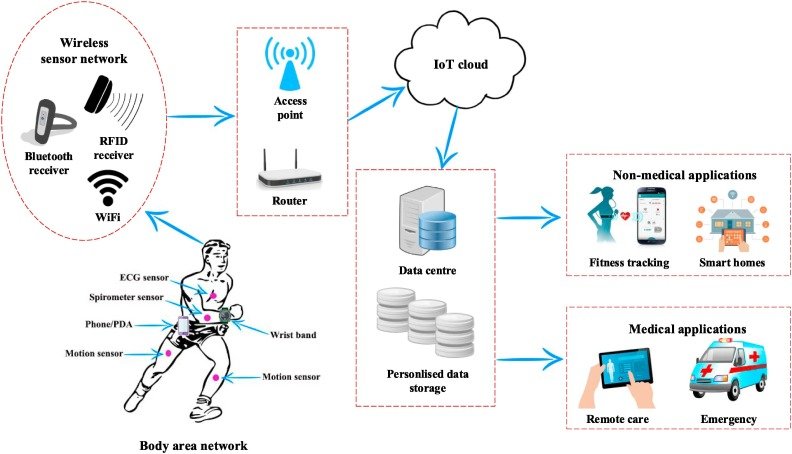
- In an emergency, such as an intensive care unit, real-time monitoring is necessary for providing fast alarms and swift actions by keeping an eye on patients’ vital signs.
- By processing data locally, telemedicine support enables remote diagnostics and virtual consultations, which benefits underprivileged or isolated locations.
- Enhanced privacy lowers the danger of data breaches by processing private patient information locally.
- Real-time patient data analysis is used in personalized medicine to provide individualized treatment strategies that enhance diagnosis and results.
2: Improved Efficiency in Manufacturing
By allowing smarter, more responsive, and economical systems, edge computing is transforming the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and manufacturing. It enables real-time analytics and low-latency monitoring using IoT sensors in smart factories by processing data locally. Hence, this improves the tracking of machine health, finds problems with the production line before they become problems, and leads to increased productivity, cost savings, and efficiency.
- By using edge computing and real-time monitoring, problems can be identified early on, reducing expensive downtime and improving maintenance plans.
- Edge computing makes it possible to analyze manufacturing data instantly, which enhances product quality and lowers defects.
- Logistics, inventory control, and supply chain efficiency are all improved by real-time tracking of assets and items.
- By analyzing energy patterns, edge computing can pinpoint locations where consumption can be cut. This leads to more economical and environmentally friendly operations.
3: Edge Computing for IoT
IoT devices are physical sensors that have limited processing power that connect to the internet. They gather data and transfer it to the cloud for analysis. Positioned at the edge of the network, edge devices serve as middlemen by providing additional processing power, storage, and local analytics. Furthermore, as 5G networks is deployed, edge computing and the Internet of Things benefit from faster bandwidth and reduced latency. This allows for real-time applications and enhanced performance. Additionally, the increased device density enables more devices to connect seamlessly. Processing sensitive data locally, lessens dependency on the cloud, and improves privacy and security. It also guarantees more dependable and effective operations, particularly in real-time scenarios like autonomous systems.
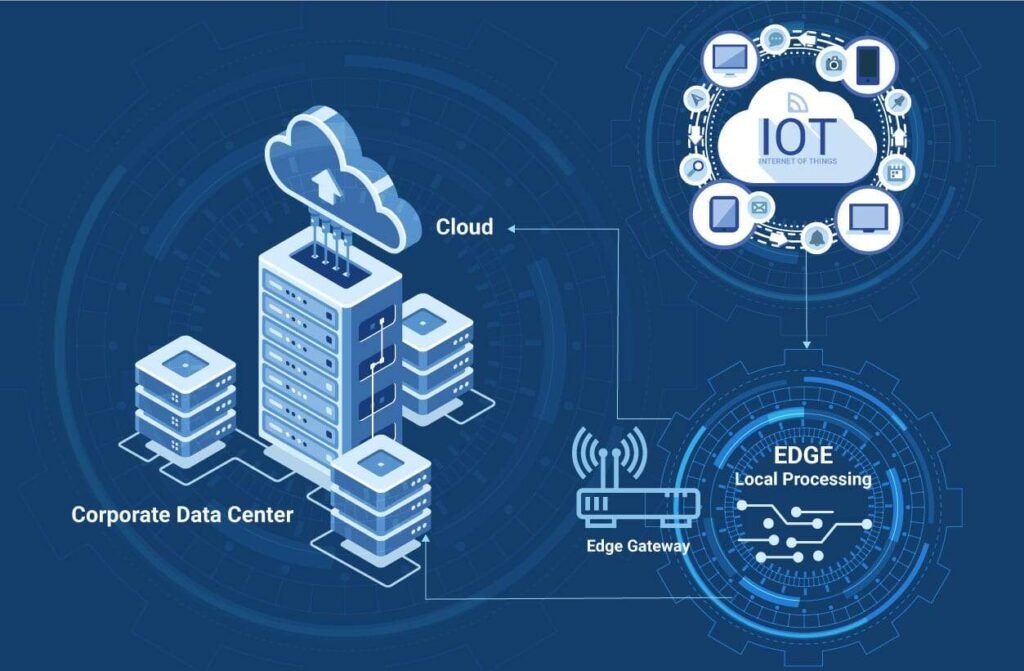
- Faster data processing made possible by edge computing shortens reaction times for vital applications like healthcare and driverless cars.
- By minimizing cloud data transfers, local data processing eases network stress and prevents congestion.
- By keeping sensitive data closer to its source, edge processing improves privacy and gives you more control over security protocols.
4: Processing Data in Autonomous Automobiles
With innovations like connected cars and driverless truck convoys, edge computing is completely changing the transportation industry. It improves navigation, lowers latency, and increases safety by allowing real-time communication between automobiles. Additionally, edge computing reduces storage requirements and bandwidth consumption, increasing the effectiveness and affordability of autonomous vehicles. By deploying this technology in-car, at network edges, or via cloud-to-edge computing, safer and more environmentally friendly transportation options can be implemented.
- By lowering latency, edge computing enables faster reaction times and lowers production floor expenses and downtime.
- With storing data in designated areas, local data processing reduces the danger of cyberattacks and guarantees adherence to data privacy laws.
- Edge computing-enabled real-time quality checks enable prompt remedial measures, preventing flaws and cutting waste for improved product quality and client satisfaction.
5- Simplifying Retail Operations
Through data processing near stores, enhanced customer experience, and operational efficiency, edge computing is transforming the retail industry. It simplifies network pressure, lowers latency, and decentralizes processing to improve performance, security, and flexibility. Furthermore, it solves bandwidth and connection issues brought on by the expansion of IoT devices, allowing for real-time data processing and quicker reaction times. Retailers can use it to monitor consumer interactions, provide individualized services, and close the gap between in-person and online experiences. By processing data locally, lowering dependency on external servers, and providing more affordable options than standard cloud architecture, edge computing also protects privacy.

- Offline Operation: This feature, which is essential for retail company continuity, guarantees ongoing operations even in the absence of a cloud connection.
- Savings: Lowers bandwidth expenses and makes it possible to employ less expensive hardware for local processing.
- Data Security and Privacy: Improves security and complies with laws like PCI DSS by keeping sensitive data on-site.
- Supply chain optimization ensures the availability of fresh food by enhancing order fulfillment, inventory management, and logistics.
FAQs
Edge computing boosts security, enables real-time decisions, and reduces reliance on cloud resources by processing data closer to its source.
5G cellular networks are influencing the future of enterprise IT since they are becoming essential to edge computing.
Edge computing can help reduce process waste from almost anything.
By bringing data sources and devices closer together, edge computing intends to reduce processing time and distance.
Wrapping It Up!
In conclusion, by improving speed, security, and real-time data processing, edge computing is changing entire sectors. Its worldwide influence is undeniable, spanning from healthcare to manufacturing, retail, and driverless vehicles. Edge Computing Global Implications provides a powerful answer to the growing need for quicker, more effective systems. It opens up possibilities for cost savings and more intelligent operations. Lastly, the future of technology appears brighter, more connected, and more efficient due to its capacity to analyze data locally and enhance decision-making. The possibilities of this shift is limitless, and it has only just begun.





